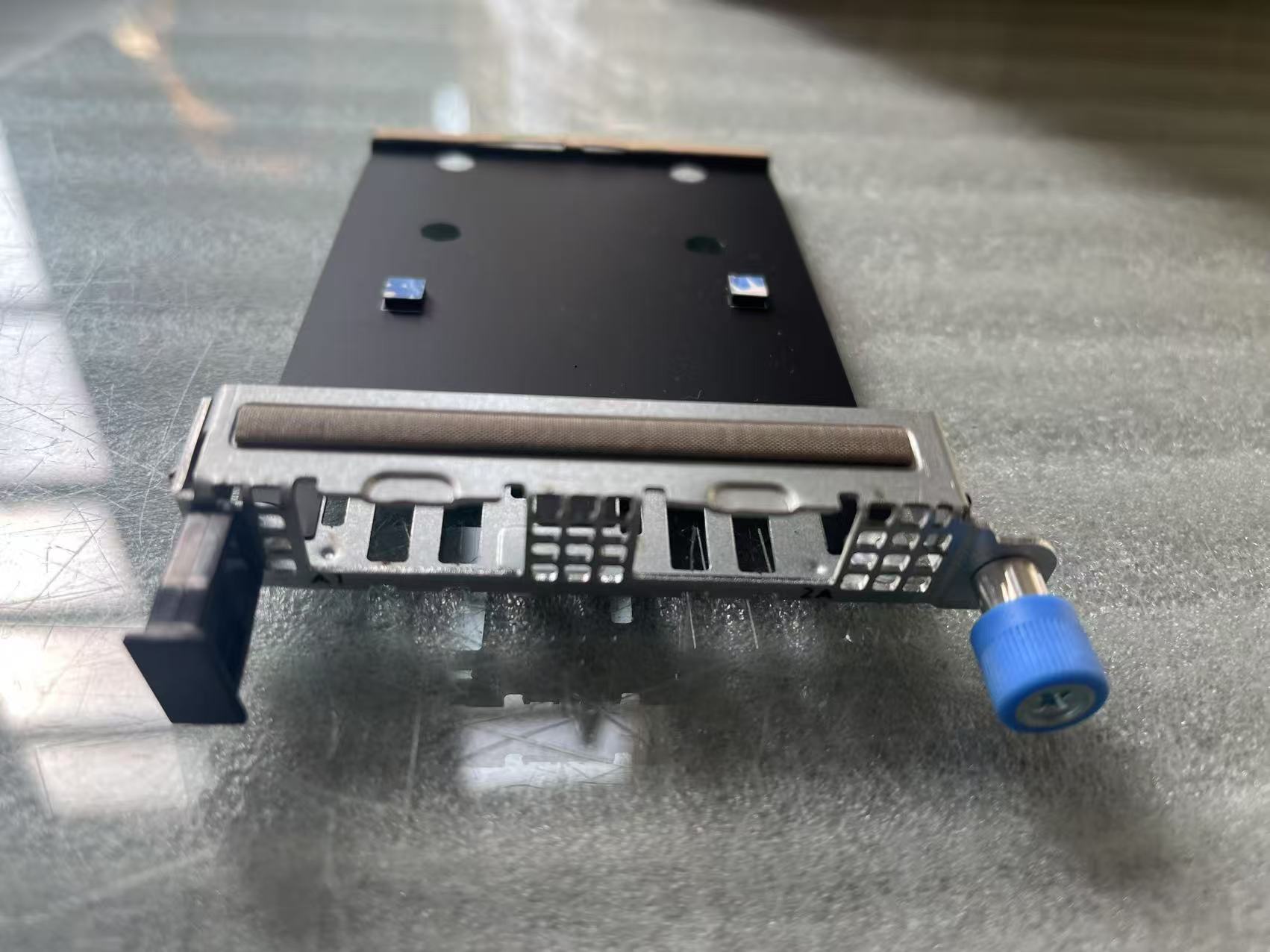
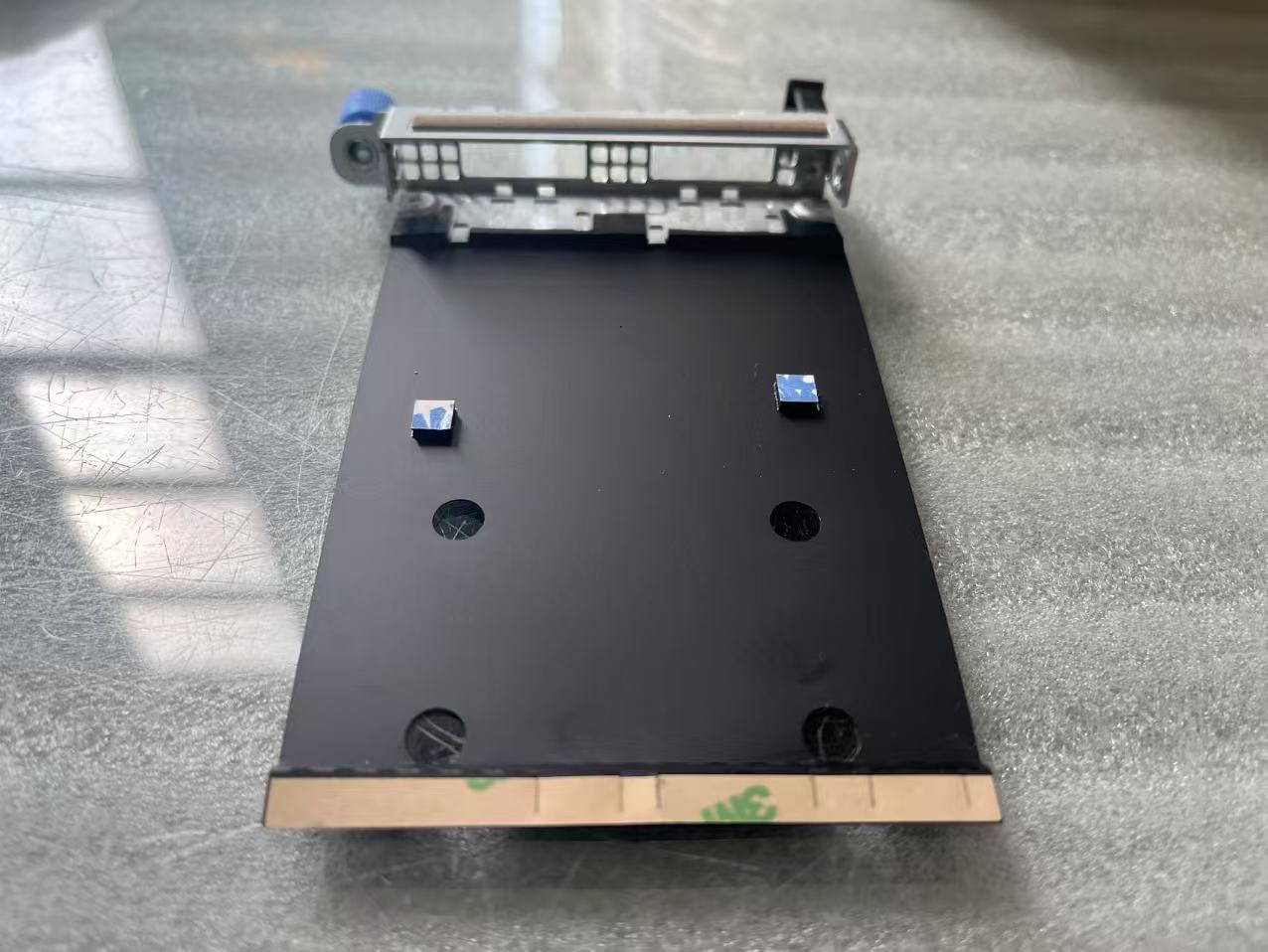
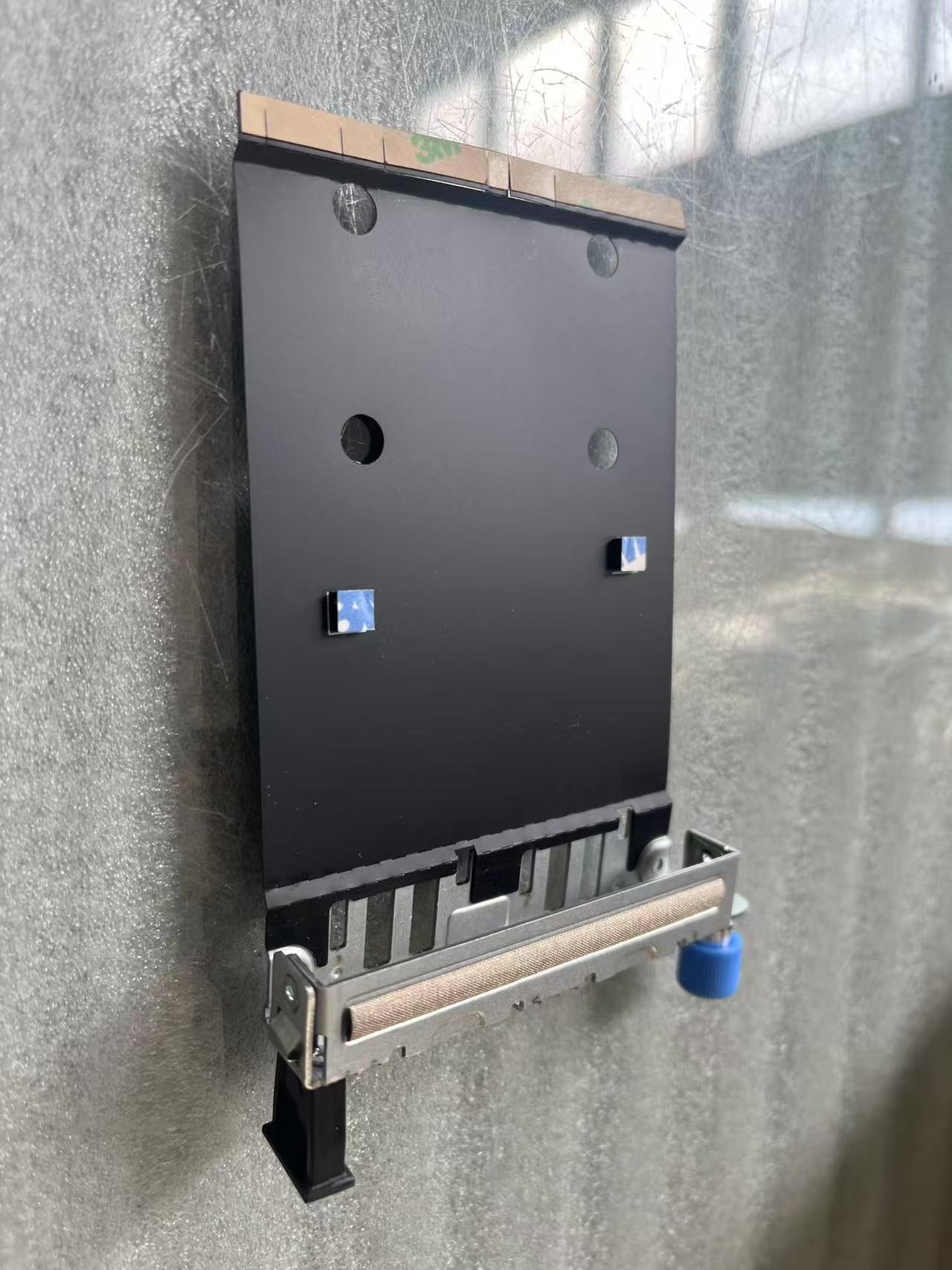
Tray,Assembly,25G-NIC,1-2
High-speed data transmission
Modern NIC supports high-speed transmission rates, such as 10G, 25G, 40G and even 100G, which can meet the needs of large data transmission and improve network performance.
Applicable to data center, cloud computing, and high-performance computing (HPC) scenarios.
High performance NIC significantly reduces the delay of data transmission through hardware acceleration and optimization design, which is suitable for applications with high real-time requirements (such as online games, financial transactions, video conferencing, etc.).
NIC supports a variety of network protocols, such as TCP/IP, UDP, and FCoE, and can adapt to different network environments and requirements.
Some nics also support RDMA (Remote Direct memory access) to further optimize data transfer efficiency.
High-end nics integrate hardware acceleration functions, such as TOE (TCP offload engine), encryption/decryption, and data compression, reducing CPU burden and improving overall system performance.
The NIC supports multiple interface types, such as PCIe, USB, and SFP+, and is compatible with different devices and network environments.
Supports multiple operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.) and is easy to integrate into existing systems.
1. Basic function
Data transfer: Transfer data between computer and network.
Signal conversion: The conversion of digital signals inside the computer into a format suitable for network transmission (such as Ethernet signals).
Protocol support: Supports multiple network protocols, such as TCP/IP, UDP, and ICMP.
Address Management: Provides MAC addresses (media access control addresses) to identify devices on the network.
By interface type:
PCIe NIC: Connects to the computer mainboard through the PCI Express interface, which is common on desktops and servers.
USB NIC: Connects to a USB port to extend network functions of a laptop or device.
Built-in NIC: Network adapter integrated on the computer motherboard.
Wireless NIC: Supports Wi-Fi connection for wireless networks.
By speed:
10/100 Mbps NIC: a traditional low-speed NIC, suitable for common office environments.
1Gbps NIC: Gigabit NIC, suitable for small and medium enterprises and home networks.
10G/25G/40G/100G NIC: High-speed NIC used in data centers, cloud computing, and high-performance computing.
By purpose:
Common NIC: Used for common network connections.
Server NIC: Supports high-performance and redundant functions, such as multi-port and link aggregation.
Intelligent NIC: Integrates hardware acceleration and supports advanced features such as uninstallation, encryption, and virtualization.
Main component
Controller chip: responsible for processing data transmission and protocol analysis.
Port: Used to connect the computer mainboard or external devices (such as PCIe, USB, SFP+, etc.).
Connector: Used to connect network cables (such as RJ45 ports) or optical fibers (such as SFP modules).
MAC address: Hardware address that uniquely identifies devices on the network.
Cache: temporarily stores data to be sent or received, improving transmission efficiency. 4. Technical features
Transmission rate: Support from 10Mbps to 100Gbps transmission rate.
Full Duplex/Half duplex: Data can be sent and received at the same time in full duplex mode, while data can be transmitted in half duplex mode only in one direction.
Hardware acceleration: Supports TOE (TCP offload engine), RDMA (remote direct memory access), encryption/decryption, and other functions.
Virtualization support: Supports SR-IOV (single root I/O virtualization) to optimize network performance in virtual machines and cloud environments.

5. Application Scenario
Home and Office network: A common NIC is used to connect to the Internet or local area network.
Data center: High-speed nics (such as 25G, 100G) are used for high-speed data transfer between servers.
Cloud Computing: Smart nics support virtualization and hardware acceleration to improve cloud service performance.
Industrial Networks: Dedicated nics are used for industrial control devices and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
High Performance Computing: nics with RDMA support are used for clustering and distributed computing.